Akbar Ghulam
Accurate & Complete behaviourial SPICE modelling
of commercial SiC Power MOSFET OF 1200V, 75A
25th EuroSimE, Catania, Italy, 2024, pp. 1-4,
DOI: 10.1109/EuroSimE60745.2024.10491420
* UNIPA Palermo (IT)
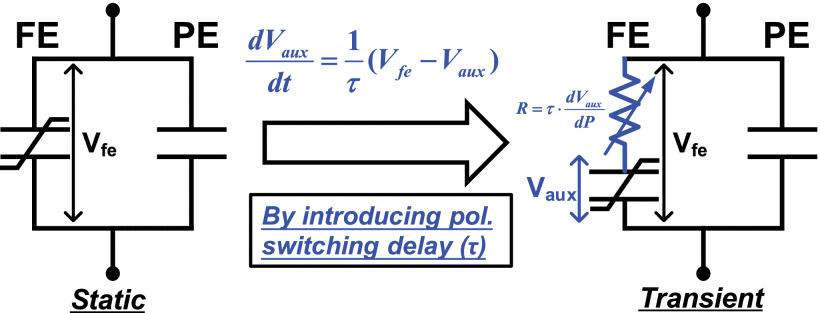
Abstract: Silicon Carbide (SiC) is proved to be an excellent replacement for Silicon in high voltage and high frequency applications due to its electro-thermal properties. Since SiC power MOSFETs have only recently been more widely available commercially, accurate simulation models are immediately required to forecast device behavior and facilitate circuit designs. The goal of this paper is to develop an accurate LTSPICE model based on a modified Enz-Krumenacher-Vittoz (EKV), MOSFET model for a 1200V, 30mΩ & 75ASiC power MOSFET “SCTW100N120G2AG” provided by STMicroelectronics that is currently on the market. The modified EKV model outperforms the reduced quadratic model by describing MOSFET behavior over different zones which are weak, moderate, and strong inversion zones with only a single equation. A wide range of experimental data was used to build the model's parameters. To estimate device performance in high frequency switching applications, the model has been expanded to include package parasitic components that include parasitic capacitances. The model's static and transient properties were simulated, and the results were compared with those acquired from the actual device.