R. Ballabrigaa, J.A. Alozya, F.N. Bandia, G. Blajb, M. Campbella, P. Christodouloua c d, V. Cocoa, A. Dordaa e, S. Emiliania h, K. Heijhoff f, E. Heijne a c, T. Hofmanna, J. Kaplona, A. Koukabh,
I. Kremastiotisa, X. Lloparta, M. Noya, A. Paternoa, M. Pillera g, J.M. Sallesseh, V. Sriskarana,
L. Tlustosa c, M. van Beuzekomf
The Timepix4 analog front-end design: Lessons learnt on fundamental limits to noise and time resolution in highly segmented hybrid pixel detectors
Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment
Volume 1045, 1 January 2023, 167489
DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.167489
a CERN, Experimental Physics Department, Meyrin, 1211, Switzerland
b SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, 94025, CA, United States
c IEAP, Czech Technical University in Prague, Prague, 11000, Czech Republic
d Department of Biomedical technology, Faculty of Biomedical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, nam. Sitna 3105, Kladno, 272 01, Czech Republic
e KIT - Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute for Data Processing and Electronics (IPE), Hermann-von-Helmholtz-Platz 1, Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, 76344, Germany
f Nikhef, Science Park 105, Amsterdam, 1098, Netherlands
g Institute of Electronics, Graz University of Technology, Graz, 8010, Austria
h Electron Device Modeling and Technology Laboratory (EDLAB), EPFL, Switzerland
Abstract: This manuscript describes the optimization of the front-end readout electronics for high granularity hybrid pixel detectors. The theoretical study aims at minimizing the noise and jitter. The model presented here is validated with both circuit post layout simulations and measurements on the Timepix4 Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). The analog front-end circuit and the procedure to optimize the dimensions of the main transistors are described with detail. The Timepix4 is the most recent ASIC designed in the framework of the Medipix4 Collaboration. It was manufactured in 65 nm CMOS process, and consists of a four side buttable matrix of 448X512 pixels with 55µm pitch. The analog front-end has a gain of 36 mV/ke- when configured in High Gain Mode, and 20 mV/ke- when configured in Low Gain Mode. The Equivalent Noise Charge (ENC) is ~68e-rms and ~80e-rms in High Gain Mode and in Low Gain Mode respectively. In event driven mode, the incoming hits can be time stamped within a 200ps time bin and the chip can deal with a maximum flux of 3.6MHz mm-2s-1. In photon counting mode, the chip can deal with up to 5GHz mm-2s-1. The routine designed to optimize the Timepix4 front-end is then used to analyze the performance limits in terms of jitter and noise for Charge Sensitive Amplifiers in pixel detectors.

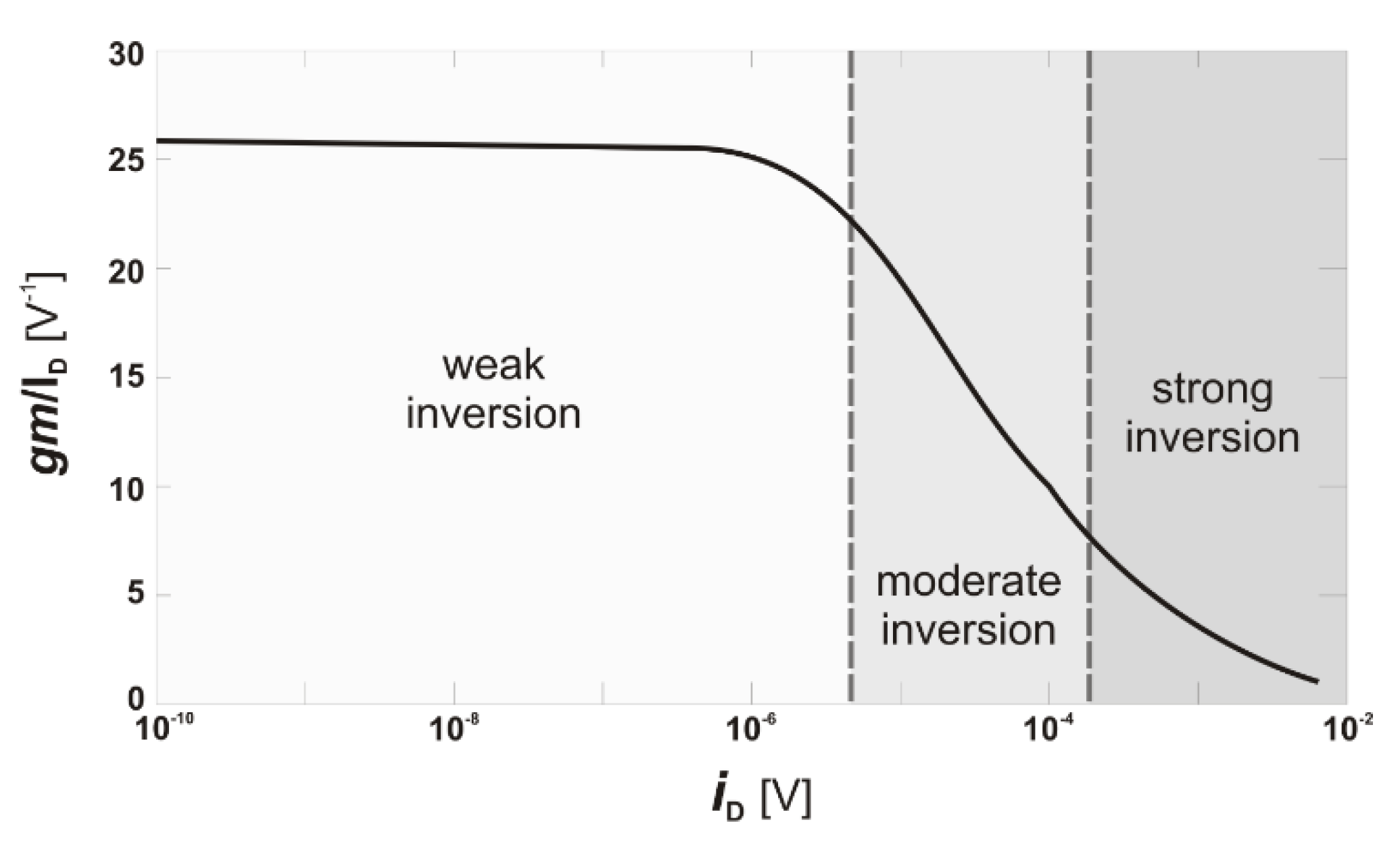
Fig: Transconductance that can be obtained for the input transistor as an EKV function of the Inversion Coefficient (IC). The asymptotes for the velocity without and with velocity saturation are shown.
Acknowledgments: The authors would like to acknowledge the Medipix Collaborations for their continuous support in the design of hybrid pixel detector readout chips.